QRegion¶

Synopsis¶
Functions¶
def
__add__(r)def
__add__(r)def
__and__(r)def
__and__(r)def
__eq__(r)def
__iadd__(r)def
__iadd__(r)def
__ior__(r)def
__isub__(r)def
__ixor__(r)def
__mul__(, m)def
__mul__(, m)def
__ne__(r)def
__or__(r)def
__sub__(r)def
__xor__(r)def
begin()def
boundingRect()def
cbegin()def
cend()def
contains(p)def
contains(r)def
end()def
intersected(r)def
intersected(r)def
intersects(r)def
intersects(r)def
isEmpty()def
isNull()def
rectCount()def
rects()def
setRects(rect, num)def
subtracted(r)def
swap(other)def
translate(dx, dy)def
translate(p)def
translated(dx, dy)def
translated(p)def
united(r)def
united(r)def
xored(r)
Detailed Description¶
QRegionis used withsetClipRegion()to limit the paint area to what needs to be painted. There is also arepaint()function that takes aQRegionparameter.QRegionis the best tool for minimizing the amount of screen area to be updated by a repaint.This class is not suitable for constructing shapes for rendering, especially as outlines. Use
QPainterPathto create paths and shapes for use withQPainter.
QRegionis an implicitly shared class.
Creating and Using Regions¶
A region can be created from a rectangle, an ellipse, a polygon or a bitmap. Complex regions may be created by combining simple regions using
united(),intersected(),subtracted(), orxored()(exclusive or). You can move a region usingtranslate().You can test whether a region
isEmpty()or if itcontains()aQPointorQRect. The bounding rectangle can be found withboundingRect().Iteration over the region (with
begin(),end(), or C++11 ranged-for loops) gives a decomposition of the region into rectangles.Example of using complex regions:
class MyWidget (QWidget): # ... def paintEvent(self): r1 = QRegion(QRect(100, 100, 200, 80), QRegion.Ellipse) # r1: elliptic region ) r2 = QRect(100, 120, 90, 30) # r2: rectangular region r3 = r1.intersected(r2) # r3: intersection painter = QPainter(self) painter.setClipRegion(r3) ... # paint clipped graphicsSee also
- class PySide2.QtGui.QRegion¶
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion(bitmap)
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion(pa[, fillRule=Qt.OddEvenFill])
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion(r[, t=Rectangle])
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion(region)
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion(x, y, w, h[, t=Rectangle])
- param w:
int
- param x:
int
- param y:
int
- param h:
int
- param fillRule:
- param bitmap:
- param region:
- param r:
- param t:
- param pa:
Constructs an empty region.
See also
Constructs a rectangular or elliptic region.
If
tisRectangle, the region is the filled rectangle (x,y,w,h). IftisEllipse, the region is the filled ellipse with center at (x+w/ 2,y+h/ 2) and size (w,``h`` ).
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.RegionType¶
Specifies the shape of the region to be created.
Constant
Description
QRegion.Rectangle
the region covers the entire rectangle.
QRegion.Ellipse
the region is an ellipse inside the rectangle.
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.begin()В¶
- Return type:
Returns a
const_iteratorpointing to the beginning of the range of non-overlapping rectangles that make up the region.The union of all the rectangles is equal to the original region.
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.boundingRect()В¶
- Return type:
Returns the bounding rectangle of this region. An empty region gives a rectangle that is
isNull().
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.contains(p)В¶
- Parameters:
p вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QPoint- Return type:
bool
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.contains(r)
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QRect- Return type:
bool
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.end()В¶
- Return type:
Returns a
const_iteratorpointing to one past the end of non-overlapping rectangles that make up the region.The union of all the rectangles is equal to the original region.
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.intersected(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QRect- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.intersected(r)
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.intersects(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QRect- Return type:
bool
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.intersects(r)
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
bool
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.isEmpty()В¶
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the region is empty; otherwise returnsfalse. An empty region is a region that contains no points.Example:
r1 = QRegion(10, 10, 20, 20) r1.isNull() // false r1.isEmpty() // false r2 = QRegion(40, 40, 20, 20) r3 = QRegion() r3.isNull() // true r3.isEmpty() // true r3 = r1.intersected(r2) // r3: intersection of r1 and r2 r3.isNull() // false r3.isEmpty() // true r3 = r1.united(r2) // r3: union of r1 and r2 r3.isNull() // false r3.isEmpty() // false
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.isNull()В¶
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the region is empty; otherwise returnsfalse. An empty region is a region that contains no points. This function is the same asisEmptySee also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__ne__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif this region is different from theotherregion; otherwise returnsfalse.
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__and__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QRect- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__and__(r)
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__mul__(m)В¶
- Parameters:
m вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QMatrix- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__mul__(m)
- Parameters:
m вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QTransform- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__add__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QRect- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__add__(r)
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__iadd__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QRect- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__iadd__(r)
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__sub__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
Applies the
subtracted()function to this region andr.r1-r2is equivalent tor1.subtracted(r2).See also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__isub__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
Applies the
subtracted()function to this region andrand assigns the result to this region.r1-=r2is equivalent tor1 = r1.subtracted(r2).See also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__eq__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the region is equal tor; otherwise returns false.
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__xor__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
Applies the
xored()function to this region andr.r1^r2is equivalent tor1.xored(r2).See also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__ixor__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
Applies the
xored()function to this region andrand assigns the result to this region.r1^=r2is equivalent tor1 = r1.xored(r2).See also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__or__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
Applies the
united()function to this region andr.r1|r2is equivalent tor1.united(r2).See also
united()operator+()
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.__ior__(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
Applies the
united()function to this region andrand assigns the result to this region.r1|=r2is equivalent tor1 = r1.united(r2).See also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.rectCount()В¶
- Return type:
int
Returns the number of rectangles that this region is composed of. Same as
end() - begin().
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.rects()В¶
- Return type:
Note
This function is deprecated.
Use
begin()andend()instead.Returns an array of non-overlapping rectangles that make up the region.
The union of all the rectangles is equal to the original region.
See also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.setRects(rect, num)В¶
- Parameters:
rect вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QRectnum вҖ“ int
Sets the region using the array of rectangles specified by
rectsandnumber. The rectangles must be optimally Y-X sorted and follow these restrictions:The rectangles must not intersect.
All rectangles with a given top coordinate must have the same height.
No two rectangles may abut horizontally (they should be combined into a single wider rectangle in that case).
The rectangles must be sorted in ascending order, with Y as the major sort key and X as the minor sort key.
See also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.subtracted(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
Returns a region which is
rsubtracted from this region.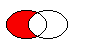
The figure shows the result when the ellipse on the right is subtracted from the ellipse on the left (
left - right).See also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.swap(other)В¶
- Parameters:
other вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion
Swaps region
otherwith this region. This operation is very fast and never fails.
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.translate(p)В¶
- Parameters:
p вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QPoint
This is an overloaded function.
Translates the region
point.x() along the x axis andpoint.y() along the y axis, relative to the current position. Positive values move the region to the right and down.Translates to the given
point.
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.translate(dx, dy)
- Parameters:
dx вҖ“ int
dy вҖ“ int
Translates (moves) the region
dxalong the X axis anddyalong the Y axis.
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.translated(p)В¶
- Parameters:
p вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QPoint- Return type:
This is an overloaded function.
Returns a copy of the regtion that is translated
p.x() along the x axis andp.y() along the y axis, relative to the current position. Positive values move the rectangle to the right and down.See also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.translated(dx, dy)
- Parameters:
dx вҖ“ int
dy вҖ“ int
- Return type:
Returns a copy of the region that is translated
dxalong the x axis anddyalong the y axis, relative to the current position. Positive values move the region to the right and down.See also
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.united(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtCore.QRect- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.united(r)
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
- PySide2.QtGui.QRegion.xored(r)В¶
- Parameters:
r вҖ“
PySide2.QtGui.QRegion- Return type:
Returns a region which is the exclusive or (XOR) of this region and
r.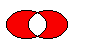
The figure shows the exclusive or of two elliptical regions.
See also
В© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
